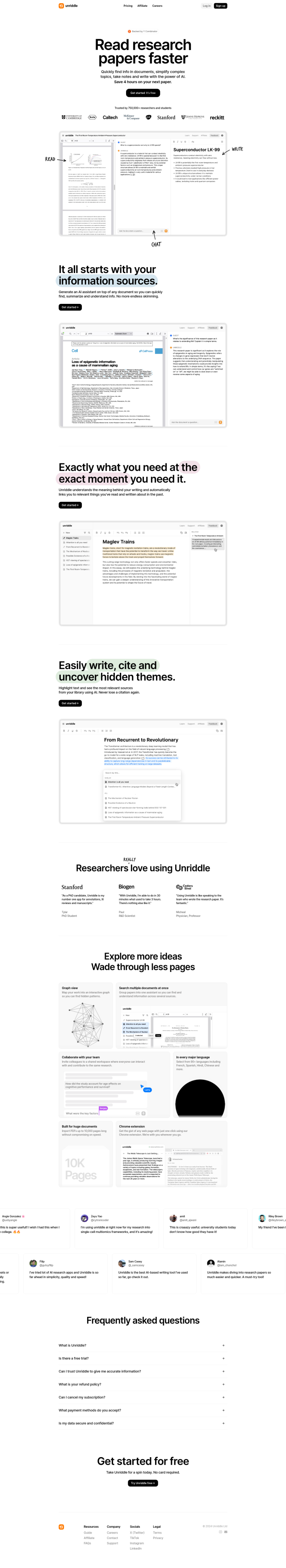
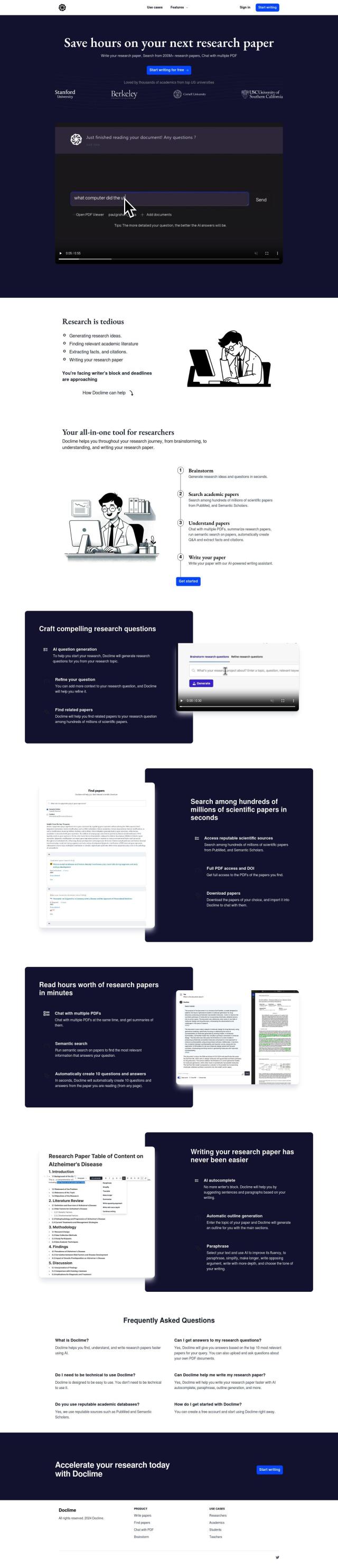
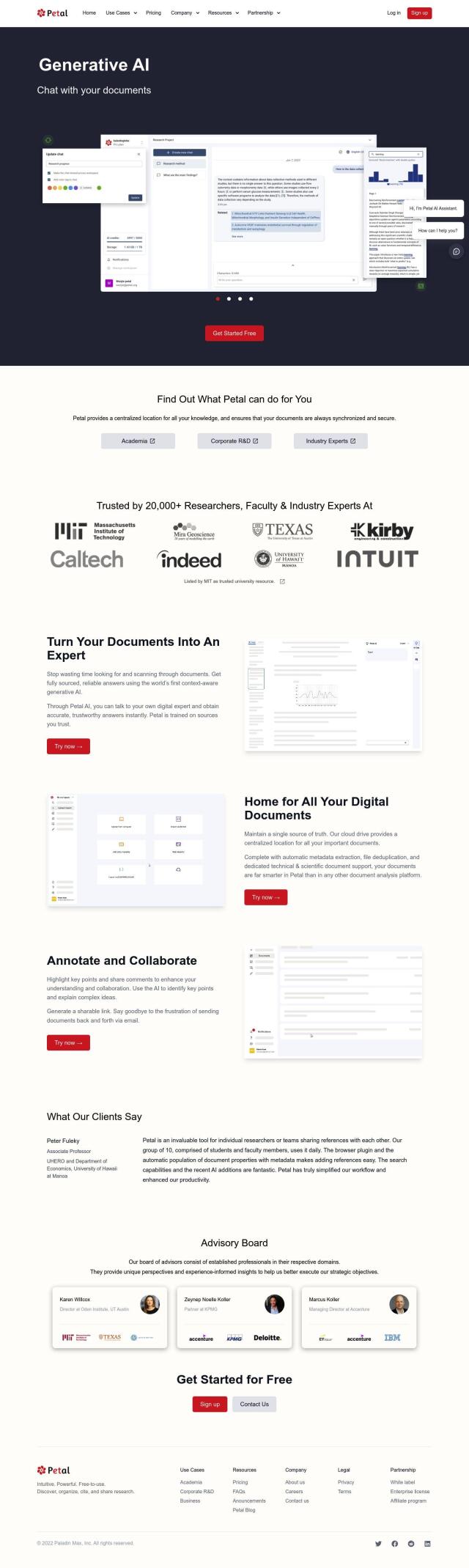
Question: Is there a cloud-based platform that allows researchers to collaborate and share annotated concepts, with persistent graph functionality, to speed up R&D in biomedicine and life sciences?

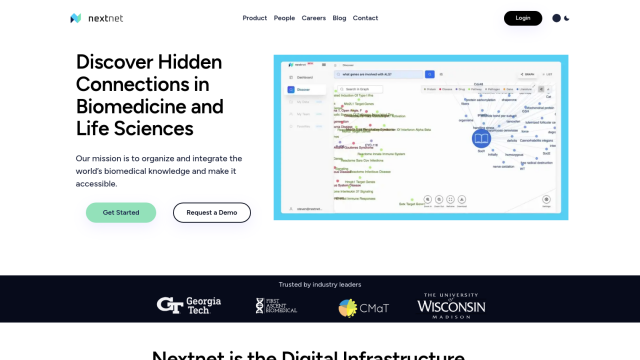
Nextnet
If you're looking for a cloud-based platform for collaboration and sharing annotated concepts, with persistent graph abilities, Nextnet is a great option for biomedicine and life sciences researchers. It's a large-scale semantic biomedical knowledge network powered by an AI ingestion engine that lets you find relationships and hypothesize new connections. The Collaborate plan lets you save, share, tag and annotate concepts with persistent graph abilities, so it's good for collaborative R&D projects.

Elicit
Another tool worth considering is Elicit, an AI research assistant that helps you find, summarize and extract information from research papers. It's geared more toward analyzing academic papers and literature reviews, but it can also find themes and concepts that could be useful for biomedicine research. Elicit's conversation interface lets you ask questions of the paper's content, which could speed up your research.
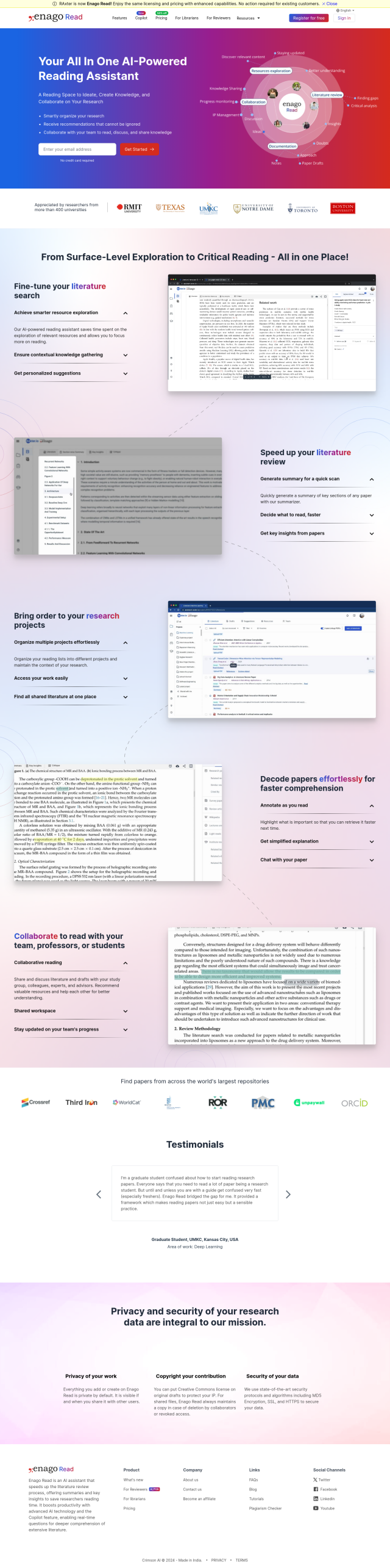
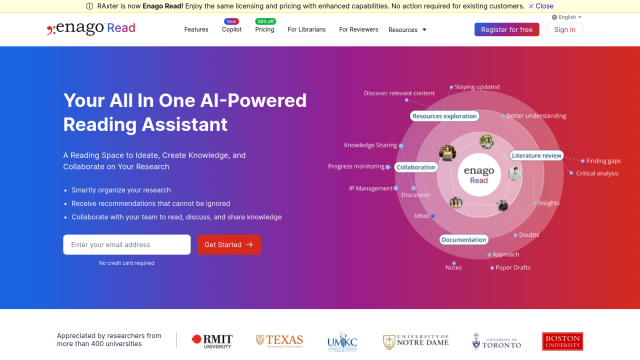
Enago Read
If you want an AI-powered assistant, Enago Read is a reading space for ideation and collaboration, a smart library for project management and collaborative tools for sharing and annotating papers. It also can generate summaries and recommend papers based on your interests, making it a good option for academic researchers trying to get a handle on their work.
Neo4j
Finally, Neo4j is a powerful graph data platform that can connect and analyze complex data structures, including knowledge graphs. It's not specifically geared for biomedicine, but graph-native abilities can be useful for handling large, complex data sets, which could be useful for integrating and contextualizing information from different sources.