Question: I'm looking for a platform that helps researchers connect the dots between different biomedical data sources to accelerate discovery.

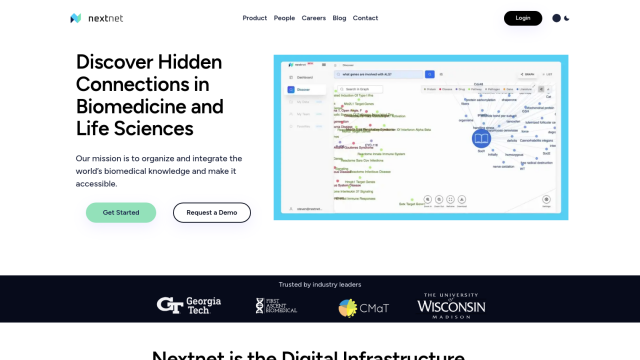
Nextnet
If you're looking for a platform to help researchers link biomedical data across different sources, Nextnet could be just the ticket. This cloud-based information retrieval system indexes biomedical knowledge from around the world and lets users search with natural language or keywords. Options like relational search, conceptual search and a large-scale semantic biomedical knowledge graph, all powered by AI, help you quickly find primary evidence and insights. It's good for integrating and contextualizing information from different data sources.
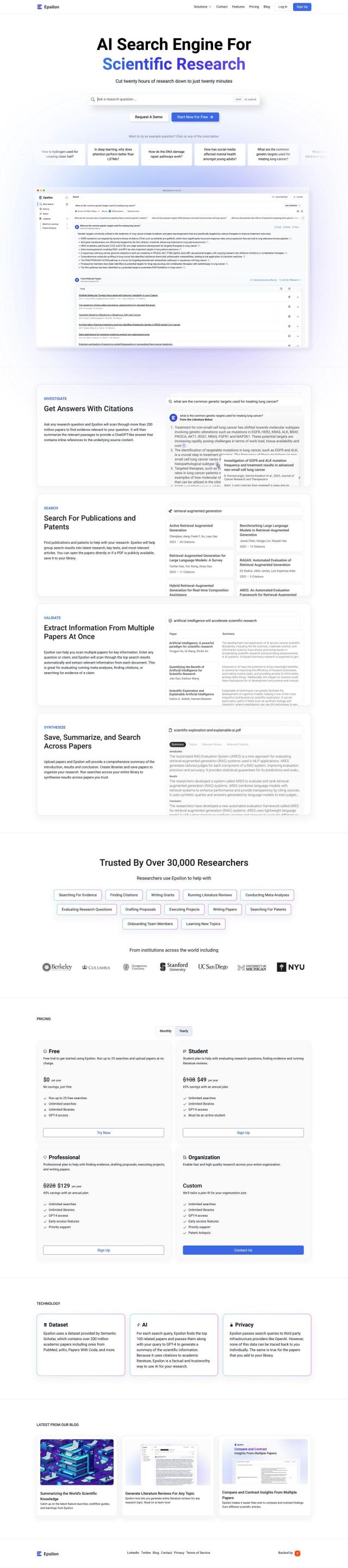
Epsilon
Another option is Epsilon, an AI-powered search engine that speeds up scientific discovery by finding relevant citations, summarizing content and synthesizing insights. It includes tools like Investigate, which offers summarized answers with inline citations, and Synthesize, which generates detailed summaries of vetted papers. More than 30,000 researchers have signed up for Epsilon, so it's a good option for organizing publications and patents to guide your research and evaluate claims.

Elicit
Elicit is another AI research assistant designed to help you quickly find, summarize and extract data from academic papers. It can search and summarize more than 125 million papers, which is useful for literature reviews and automating systematic reviews. It's particularly good for biomedicine and machine learning, where researchers need to keep up with the latest research and find themes and concepts.
OpenRead
For a more complete research experience, OpenRead indexes more than 300 million papers and indexes them in real time from more than 20,000 journals. It includes tools like Paper Espresso, which summarizes paper content, and Paper Q&A, which lets you ask questions about papers. OpenRead also includes a Related Paper Graph to show connections between papers, which can be useful for exploring and keeping up to date with research in your area.