Question: I need a system that uses AI to extract and map biomedical concepts from various data sources, including text, images, and videos.

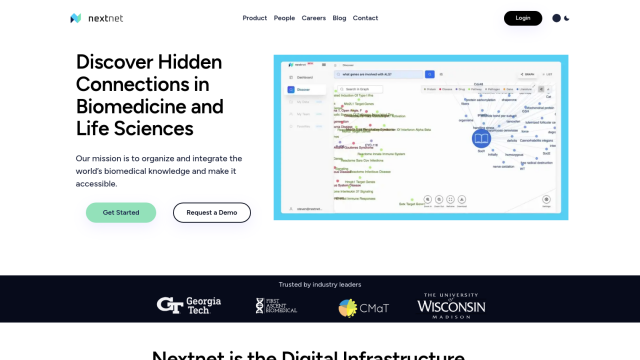
Nextnet
If you're looking for a system that uses AI to extract and map biomedical concepts from different sources of data, including text, images and video, Nextnet might be of interest. This cloud-based information retrieval system is geared for biomedicine and life sciences researchers and scientists to uncover relationships and formulate hypotheses. It aggregates and contextualizes biomedical knowledge from around the world, allowing users to perform semantic searches using natural language or keywords and tap into a large-scale semantic biomedical knowledge graph powered by an AI ingestion engine.

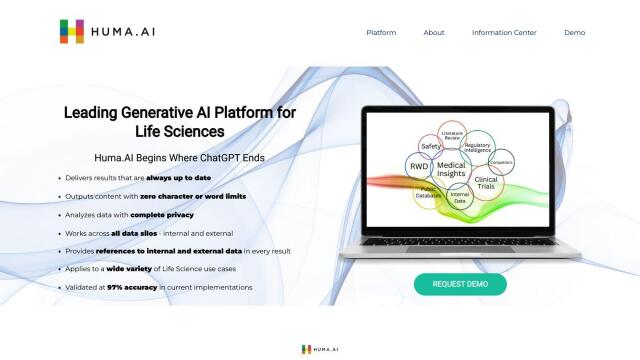
Huma.AI
Another option is Huma.AI, a generative AI platform for the life sciences industry. It's designed for medical affairs, regulatory affairs and clinical development teams to understand and interpret machine learning outputs. The platform offers real-time results with no character or word limits, full privacy and access to internal and external data sources, which makes it suitable for tasks such as improving scientific communication, understanding the competitive trial landscape and simplifying real-world data analysis.

Elicit
If you need to quickly find, summarize and extract information from academic papers, Elicit is worth a look. This AI research assistant lets you search for papers, extract information into formatted tables, discover themes and concepts and even converse with the content of papers. It's particularly useful for biomedicine and machine learning, for example with systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
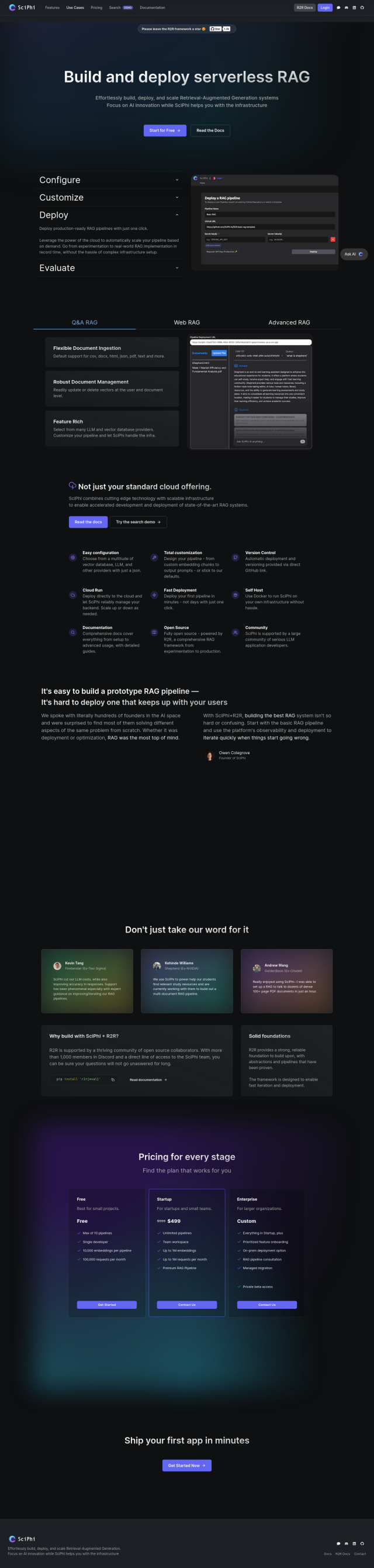
SciPhi
Last, SciPhi offers a modular information retrieval system that can be used to build and deploy Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. It offers powerful document management, flexible provider integration, dynamic scaling and deployment of state-of-the-art methods. That makes it a good option for integrating and contextualizing information from different sources of data, accelerating AI innovation and customization.